
HALCON 20.11
HALCON 20.11 was released in November, 2020, and comes with many new and improved features that help you further enhance your machine vision performance. Next to optimizations for a number of core technologies, this new version also includes a new feature called Deep OCR. With this feature you can profit from a holistic deep-learning-based approach for optical character recognition (OCR).
HALCON 20.11 is available in two editions: Steady and Progress. While the latter is available as a subscription with a six-month release cycle, the Steady edition is offered as one-time purchase.
Find more information on this version's new features below or have a look at the webinar recording of our feature presentation.

Improved Surface-based 3D-Matching
In HALCON 20.11, the core technology, edge-supported surface-based 3D-matching, is significantly faster for 3D scenes containing many objects and edges.
In addition to this speedup, the usability has been improved by removing the need to set a viewpoint.

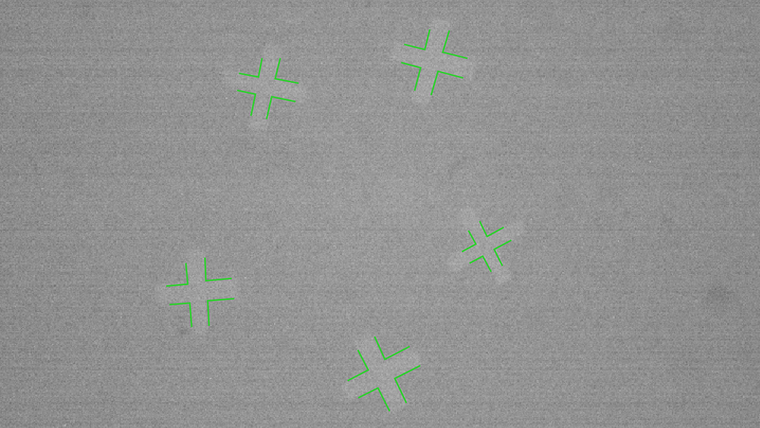
DotCode and Data Matrix Rectangular Extension
In HALCON 20.11, the data code reader has been extended by the new code type, DotCode. This type of 2D code is based on a matrix of dots. It can be printed very quickly and is especially suitable for high speed manufacturing lines, like those used in the tobacco industry.
Furthermore, the Data Matrix ECC 200 code reader now supports the Data Matrix Rectangular Extension (DMRE).

Deep OCR
Deep OCR is a holistic deep-learning-based approach for OCR. This new technology brings machine vision one step closer to human reading.
Compared to existing algorithms, Deep OCR can localize characters much more robustly, regardless of their orientation, font type and polarity. The ability to automatically group characters allows the identification of whole words. This strongly increases the recognition performance since, e.g., misinterpretation of characters with similar appearances can be avoided.

Improved Shape-based Matching
In HALCON 20.11, the core technology, shape-based matching, has been improved.
More parameters are now estimated automatically. This increases usability as well as the matching rate and robustness in low contrast and high noise situations.
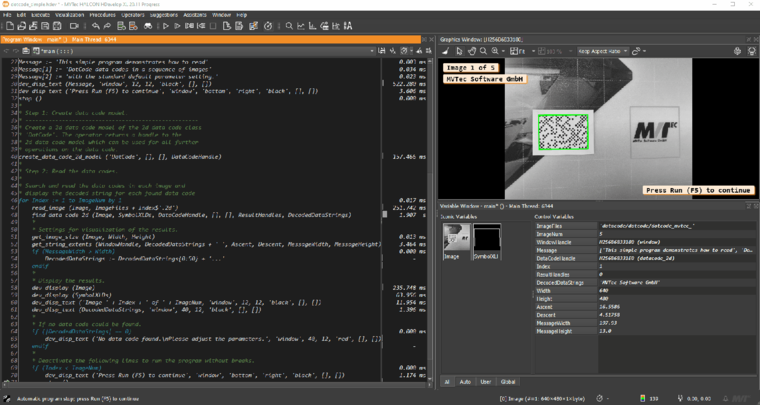
HDevelop Facelift
For enhanced usability, HALCON’s integrated development environment HDevelop has been given a facelift.
In HALCON 20.11, more options for individual configurations have been implemented, featuring e.g., a dark mode and a new modern window docking concept. Moreover, themes are now available to improve visual ergonomics and to suit individual preferences.
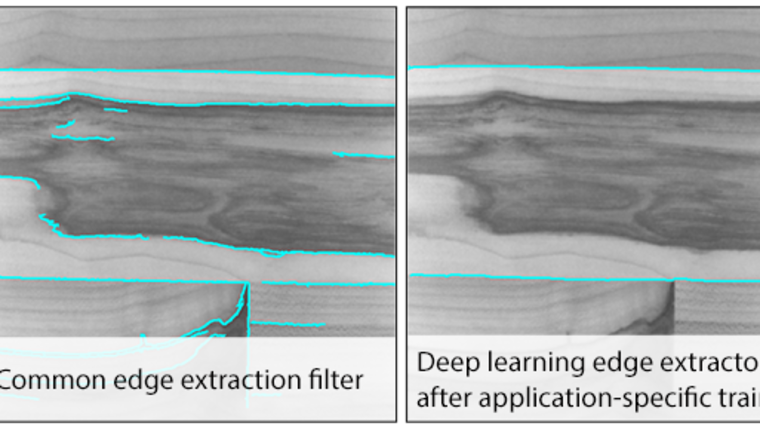

Deep Learning Edge Extraction
Deep learning edge extraction is a new and unique method to robustly extract edges (e.g., object boundaries) that comes with two major use cases.
Especially for scenarios where a variety of edges is visible in an image, it can be trained with only few images to reliably extract the desired edges. Hence, the programming effort to extract specific kinds of edges is highly reduced with this version of MVTec HALCON. Besides, the pretrained network is innately able to robustly detect edges in low contrast and high noise situations. This makes it possible to extract edges that usual edge detection filters cannot detect.
